Median Theorem Math
Rolle s theorem states that if a function f is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b such that f a f b then f x 0 for some x with a x b.
Median theorem math. Mb length of median from vertex b. It states that the sum of the squares of any two sides of any triangle equals twice the square on half the third side together with twice the square on the median bisecting the third side. In geometry apollonius s theorem is a theorem relating the length of a median of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. Ma length of median originating from vertex a.
Here s the formal definition of the theorem. To calculate the median of. W 2 b 2 2 c 2 2 a 2 4. In statistics it is the value lying at the midpoint of a data set.
8 3 44 17 12 6 there is an even amount of numbers. Even though comparison sorting n items requires ω n log n operations selection algorithms can compute the k th smallest of n items with only θ n operations. 2 42 2 62 82 4 40 4 10 3 162. This includes the median which is the n 2 th order statistic or for an even number of samples the arithmetic mean of the two middle order statistics.
3 6 8 12 17 44 add the 2 middle numbers then divide them by 2. Every triangle has exactly three medians one from each vertex and they all intersect each other at the triangle s centroid in the case of isosceles and equilateral triangles a median bisects any angle at a vertex whose two adjacent sides are equal in length. Let d be the midpoint of side b c and w a d the length of the median through a. For example if we have a triangle with the following side measurements.
Here length of median ma can be calculated as. The mathematical word median has different meanings with different operations. This can be illustrated as below. Mc length of median from vertex c.
Median to the hypotenuse is equal to half the hypotenuse by ido sarig bsc mba in today s geometry lesson we will prove that in a right triangle the median to the hypotenuse is equal to half the hypotenuse. If f is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there exists a number c in a b such that. 8 12 20 2 10 the median for this group of number is 10. The sample median efficient computation of the sample median.
Let a b c be a triangle with sides a b c. Rolle s theorem in analysis special case of the mean value theorem of differential calculus. The mean value theorem. 6 line up the numbers.
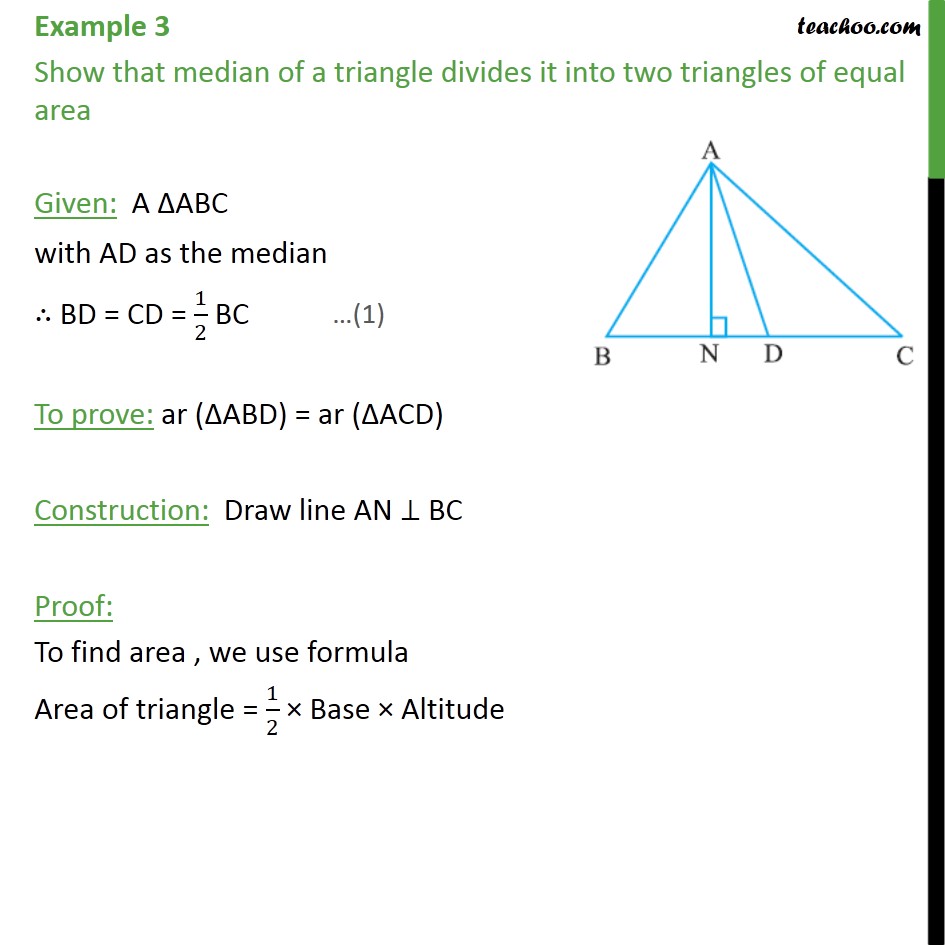
In other words if a continuous curve passes through the same y value such as the x axis twice and has a unique tangent line derivative at every point of the interval then. The median of a triangle is a line drawn from one of the vertices to the mid point of the opposite side. In geometry a median of a triangle is a line segment joining a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side thus bisecting that side. First you need to take care of the fine print.


















